Background:
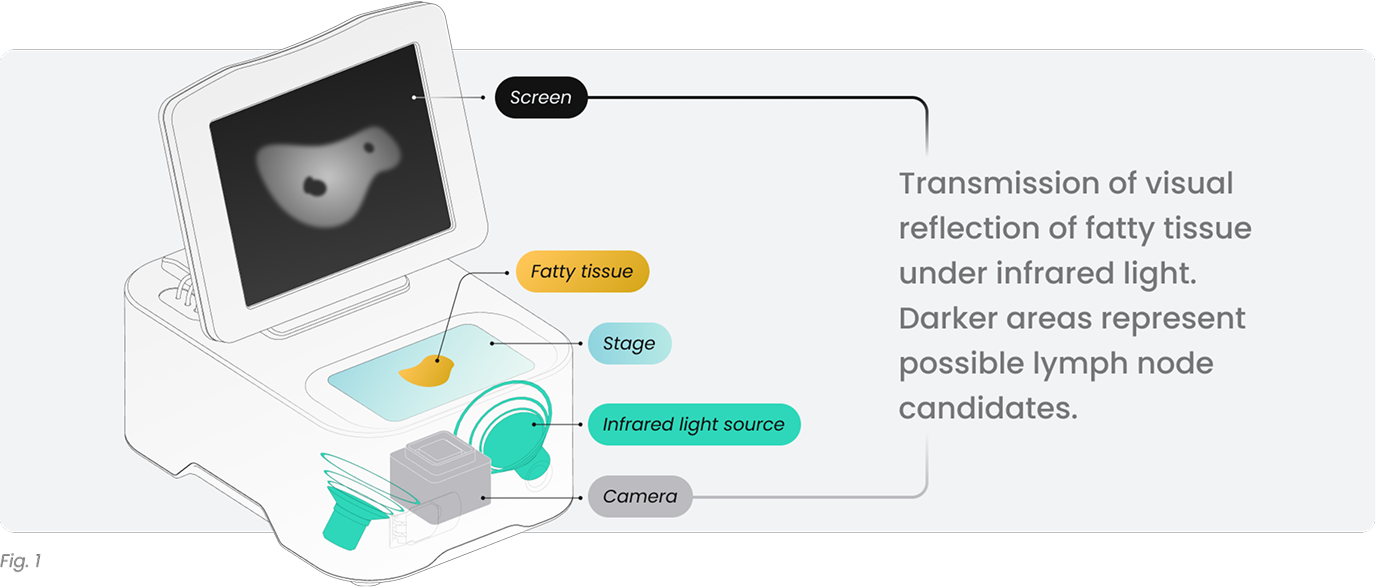
Colorectal cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related death in the US. Staging is crucial to assess prognosis and treatment options. According to AJCC guidelines, at least 12 lymph nodes are required for nodal staging. However, previous studies showed the importance of retrieving as many lymph nodes as possible. Herein, we evaluated a novel, optical imaging-based device using infrared light a.k.a. CisionVision (Cision Vision, Mountain View, CA; Fig. 1) to increase lymph node yield in colorectal cancer specimens.
Design:
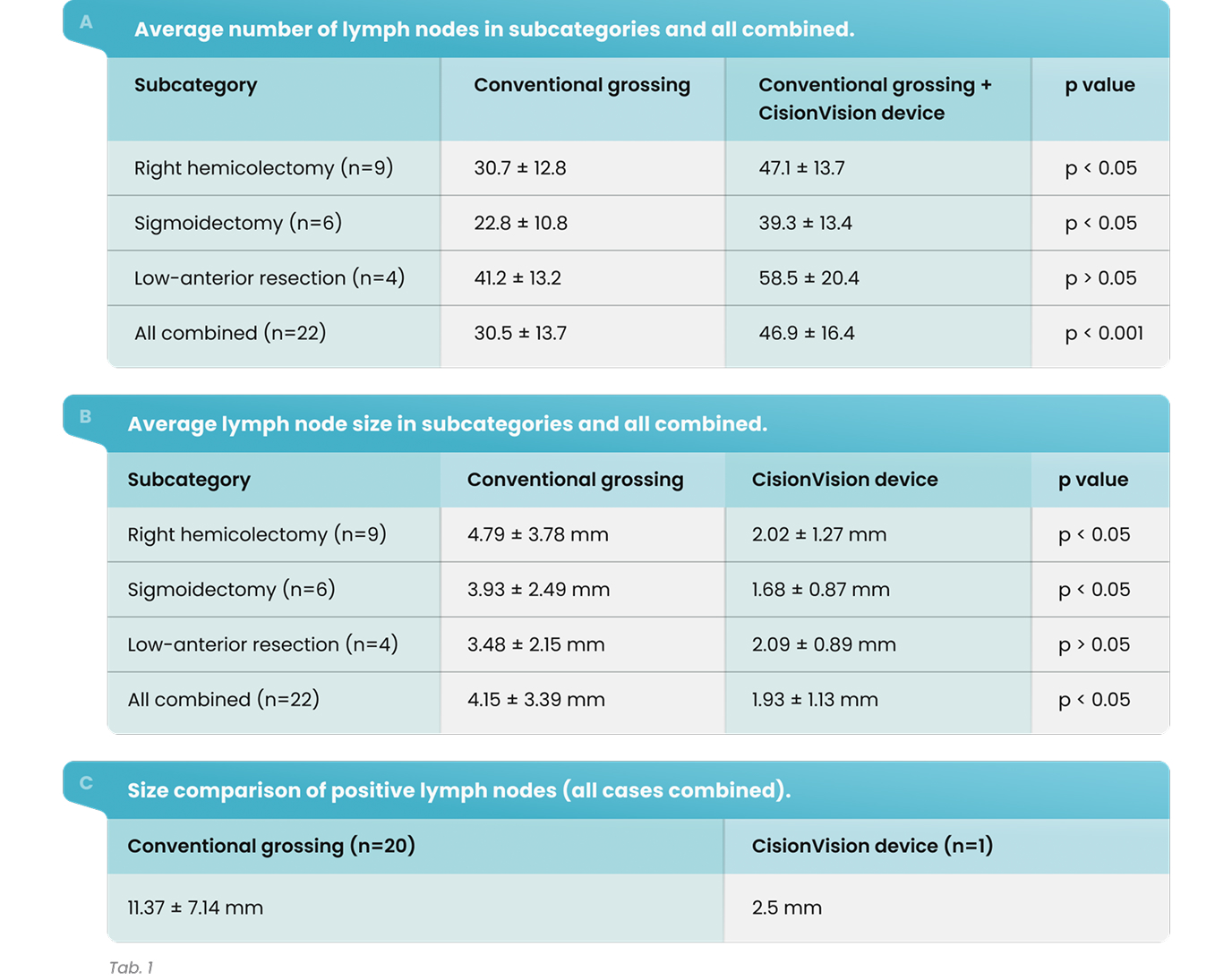
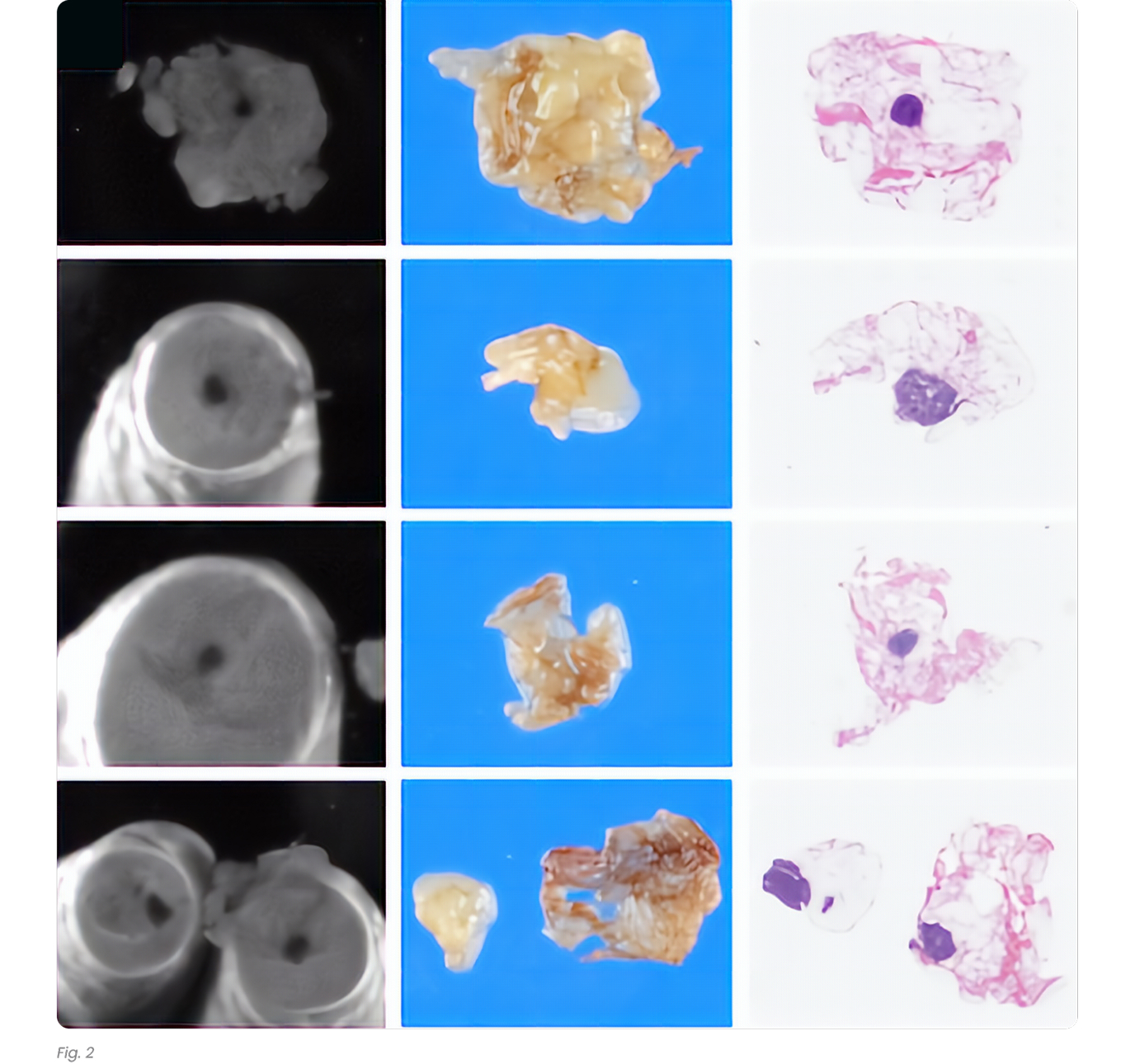
The CisionVision device has increased the lymph node yield significantly in all categories except low-anterior resection (Tab. 1). This result is likely due to a small number of subjects. The increase in lymph node yield was significant when all subjects were included in the analysis (average increase of 53%). The size of the lymph nodes was compared in each case separately, also categorically. This increase was particularly notable for smaller lymph nodes (<3 mm; Fig 2). In 19 cases, lymph nodes found by the device were significantly smaller, however in three cases, there was no significant difference. In the entire study, a total of 21 metastatic lymph nodes were harvested from 7 nodal positive cases; 20 by conventional grossing and 1 by CisionVision device where a patient was upstaged from T1 N1a M0 to T1 N1b M0.
Results:
The CisionVision device has increased the lymph node yield significantly in all categories except low-anterior resection (Tab. 1). This result is likely due to a small number of subjects. The increase in lymph node yield was significant when all subjects were included in the analysis (average increase of 53%). The size of the lymph nodes was compared in each case separately, also categorically. This increase was particularly notable for smaller lymph nodes (<3 mm; Fig 2). In 19 cases, lymph nodes found by the device were significantly smaller, however in three cases, there was no significant difference. In the entire study, a total of 21 metastatic lymph nodes were harvested from 7 nodal positive cases; 20 by conventional grossing and 1 by CisionVision device where a patient was upstaged from T1 N1a M0 to T1 N1b M0.
Results Table:
Conclusion:
The CisionVision device significantly increases lymph node yield, especially for smaller nodes, leading to potential stage changes in some cases (4.5%). While further research is needed to address limitations and explore broader clinical implications, our preliminary findings highlight its potential value in colorectal cancer pathology.
Authors
University of Chicago Medical Center/NorthShore University HealthSystem
Chicago, IL, United States
NorthShore University HealthSystem
Chicago, IL, United States
NorthShore University HealthSystem
Chicago, IL, United States
NorthShore University HealthSystem
Franklin Park, IL, United States
NorthShore University HealthSystem
Libertyville, IL, United States
