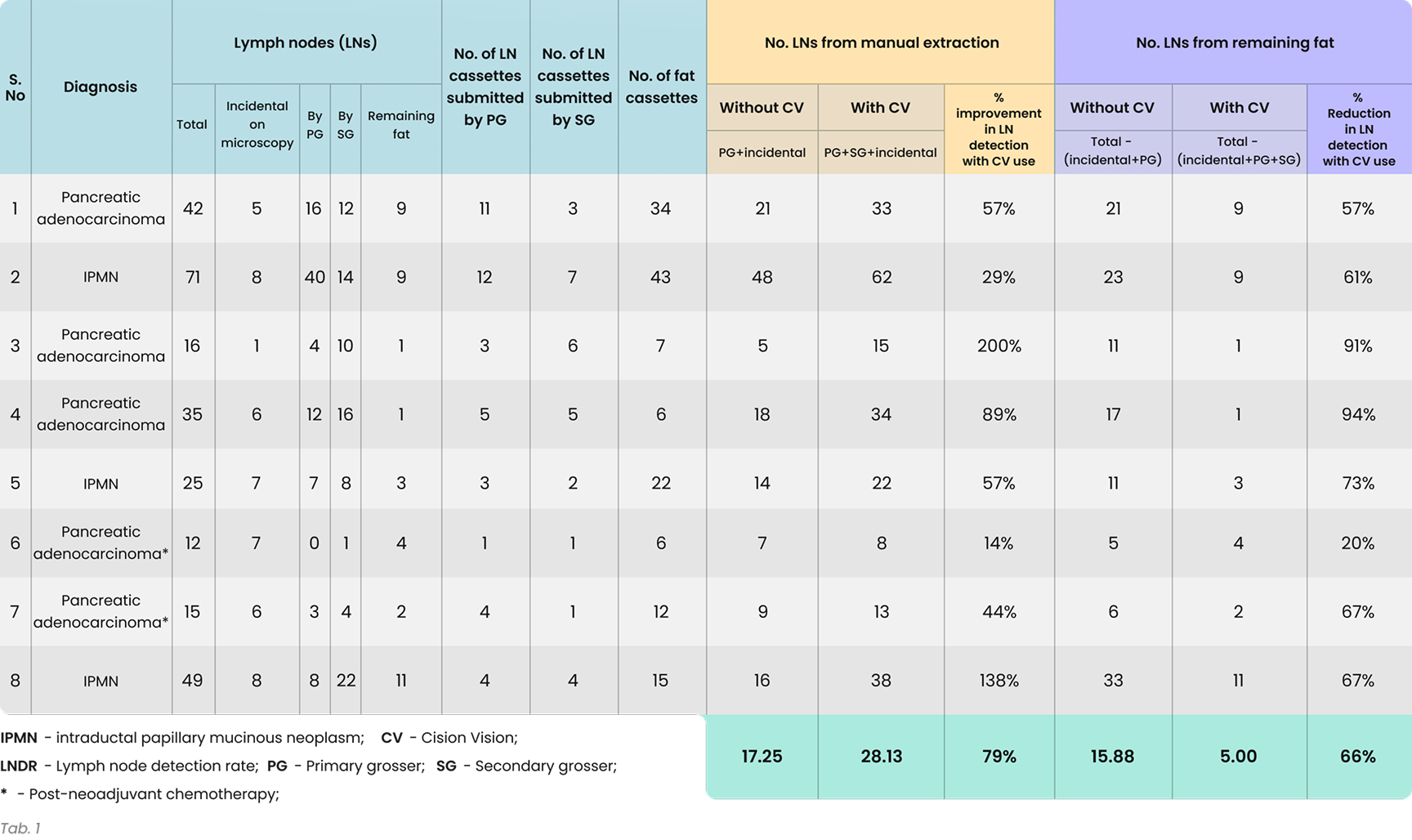
Background:
Accurate staging and prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma rely on the precise identification of regional lymph nodes (LNs). The AJCC 8th edition classifies LNs into N1 & N2 stages based on the number of LNs involved, making LN identification critical. A smaller number of LNs carries the risk of under-staging the patient while reevaluating LNs and submitting fat fragments risks overcounting LNs and upstaging the patient. CisionVision (Cision Vision, CA) (CV) is a real-time shortwave infrared imaging device to locate lymph nodes by highlighting water content contrast (Fig. 1). This study explores the utility of CV in increasing LN detection and minimizing fat submission in pancreatic resection cases.
Design:
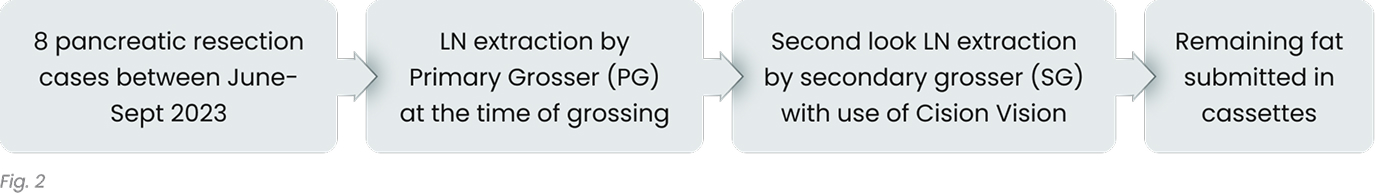
We prospectively enrolled 8 pancreatic resection cases (4 Whipple & 4 distal pancreatectomy) from June to September 2023. Primary grossers (PG) with varying levels of expertise identified LNs manually. Subsequently, a single secondary grosser (SG) utilized CV to extract additional LNs, and the remaining fat was submitted for evaluation (Fig. 2). The average number of LNs for manual extraction, remaining fat, intended LN cassettes, and fat cassettes were calculated. Incidental LNs found microscopically were included in PGs’ LN count.
Results:
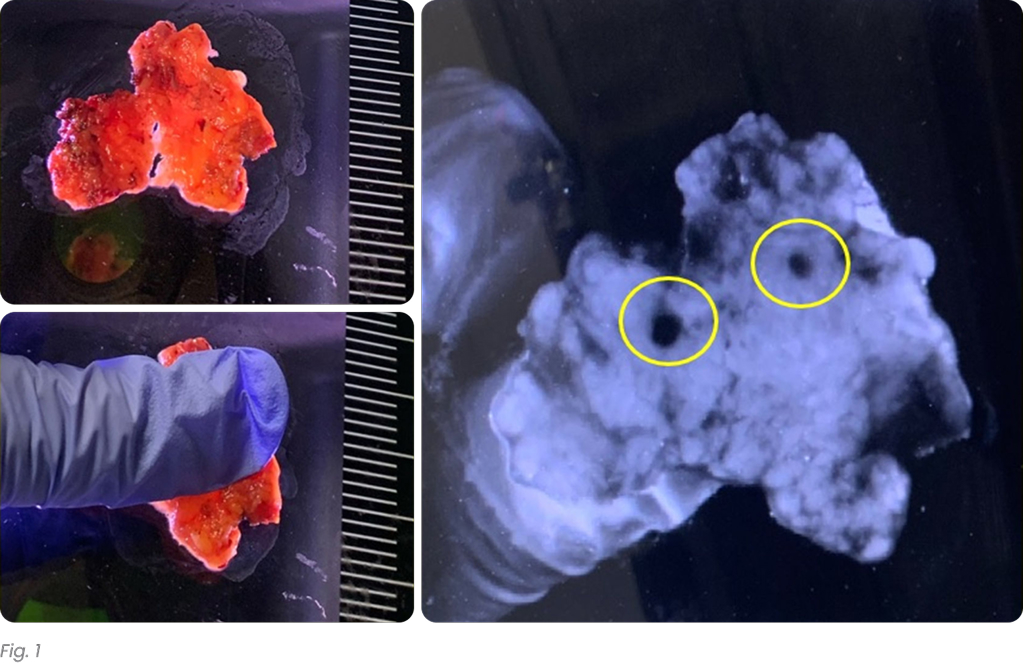
The CisionVision device has increased the lymph node yield significantly in all categories except low-anterior resection (Tab. 1). This result is likely due to a small number of subjects. The increase in lymph node yield was significant when all subjects were included in the analysis (average increase of 53%). The size of the lymph nodes was compared in each case separately, also categorically. This increase was particularly notable for smaller lymph nodes (<3 mm; Fig 2). In 19 cases, lymph nodes found by the device were significantly smaller, however in three cases, there was no significant difference. In the entire study, a total of 21 metastatic lymph nodes were harvested from 7 nodal positive cases; 20 by conventional grossing and 1 by CisionVision device where a patient was upstaged from T1 N1a M0 to T1 N1b M0.
Conclusion:
In our Our experience, CV use in pancreatic resection cases demonstrated a 79% increase in LN extraction and a 66% reduction in LN detection in remaining fat. This improvement has the potential to eliminate the need for remaining fat submission, leading to reduced costs, improved grosser accuracy, and ultimately better patient outcomes by more precise staging, and tailored treatment approaches. However, we acknowledge the small sample size of the study, further large-scale validation using CV at the time of initial grossing is underway, recruiting more cases and various organ resections.
Authors
University of Chicago NorthShore
Des Plaines, IL, United States
NorthShore University HealthSystem
Libertyville, IL, United States
NorthShore University HealthSystem
Chicago, IL, United States